
Robert Coggeshall and Cliff Spencer wrote the original subsystem around 1980 at the Department of Computer Science at SUNY/Buffalo.
It can also be configured to permit passing arguments or multiple commands.
SUDO SU RUN COMMAND PASSWORD
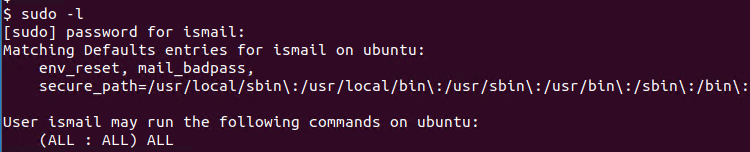
The configuration file offers detailed access permissions, including enabling commands only from the invoking terminal requiring a password per user or group requiring re-entry of a password every time or never requiring a password at all for a particular command line. After authentication, and if the configuration file (typically /etc/sudoers) permits the user access, the system invokes the requested command. Unlike the similar command su, users must, by default, supply their own password for authentication, rather than the password of the target user.
SUDO SU RUN COMMAND MANUAL
The current Linux manual pages for su define it as "substitute user", making the correct meaning of sudo "substitute user, do", because sudo can run a command as other users as well. It originally stood for "superuser do", as that was all it did, and it is its most common usage however, the official Sudo project page lists it as "su 'do' ". In this tutorial you have learned Linux su command with useful examples.Sudo ( / s uː d uː/ or / ˈ s uː d oʊ/ ) is a program for Unix-like computer operating systems that enables users to run programs with the security privileges of another user, by default the superuser.
In that condition, su provides you -c option to run command as another user without actually switching the shell. Sometimes, you may only need to switch user to run a single or few commands only. The sudo privileged users can also prefixed sudo with su command. The current environment is passed to the new shell with effective environment variables to switched user.This is used to provide an environment similar to what the user got at direct login Using hyphen (-) with switching invoke login shell scripts.Invoke the su command without username becomes the superuser (root).whoami # Output: rahul su - root # Become root user whoami # Output: root Then switch to root user with su command. I’m Logged in to my system with user ‘root’, verified the identify using whoami command.

This tutorial will help you understand the uses of Linux su command with examples. It is an frequently used command mostly by the Linux terminal users. Basically, the su command is used to change current logged in user to another user without logged out from system. When invoked without a username, su defaults switch to the super user.
This command is used to become another user during a login session. The su command is also known as switch user.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
